New disaster management software released worldwide
8 April 2014
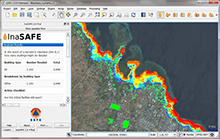
Screen capture from the InaSAFE
2.0 software, showing likely tsunami
impacts from a hypothetical magnitude
8.1 earthquake on Maumere, Flores
in Indonesia.
Geoscience Australia has contributed to a new version of software that can predict the potential social and human impact of natural disasters.
Released overnight in Indonesia, the updated version of InaSAFE 2.0 was jointly developed by Indonesia's National Disaster Management Agency (BNPB), Australian Government agencies and the World Bank.
Dr Syamsul Maarif, the Head of BNPB, said that the InaSAFE tools will help improve disaster preparedness in Indonesia by providing a new way to combine scientific hazard information and community knowledge on disaster risk.
"It enables production of realistic natural hazard impact scenarios for better planning, preparedness and response training activities, by incorporating a range of natural hazard information, such as earthquake, volcanoes, tsunami or flood; and exposure data, such as the spatial distribution of population, roads or critical infrastructure," Dr Maarif said.
Australia's Minister-Counsellor for Development Cooperation in Indonesia, Jean-Bernard Carrasco, said InaSAFE 2.0 includes the ability to work with road data, including a capability to download roads directly from the online mapping tool OpenStreetMap (OSM). The new functions could help when planning possible evacuation and emergency response routes.
"With the help of Australian Government agency Geoscience Australia and the Australia-Indonesia facility for Disaster Reduction, over 1.3 million buildings have already been mapped in OSM and this data is being incorporated into InaSAFE", Mr Carrasco said.
The updated software is compatible with the free and open source Geographic Information System QGIS 2.0, and allows users to import spatial data from remote sources and create custom impact map templates.
The World Bank, through its Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery is facilitating use of InaSAFE across the world in Africa and to countries such as Sri Lanka and Pakistan. Dr Jim Y Kim, President of the World Bank, recently listed use of InaSAFE as one of the Seven Steps to Surviving a Disaster.
InaSAFE 2.0 is free and open source software that provides disaster managers with a simple but rigorous tool for evidence-based disaster planning.




