Ginan: GNSS Analysis Centre Software
Page last updated:4 October 2023
Ginan is Geoscience Australia’s Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Analysis Centre Software that delivers a real-time positioning correction service and additional positioning products through open-source software, to enable precise point positioning.
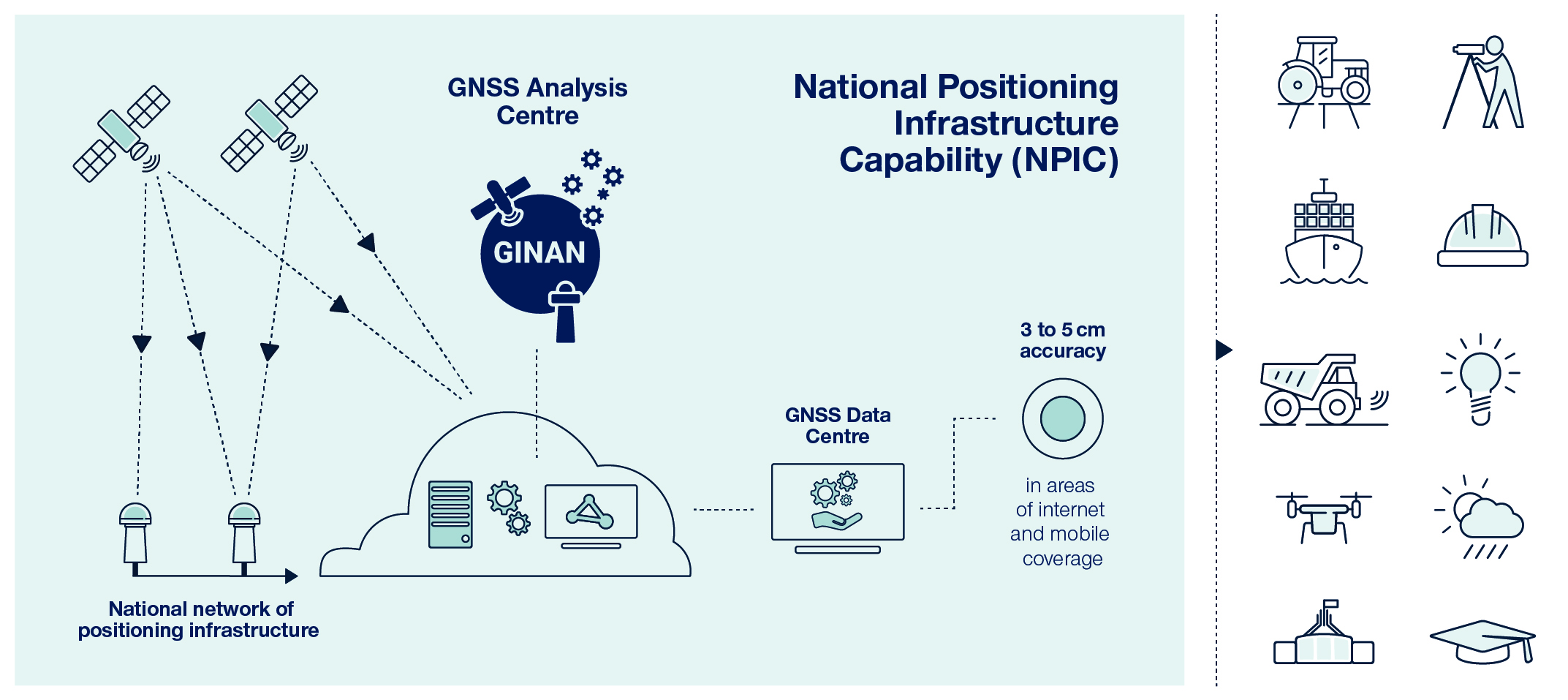
Within the NPIC ecosystem, Ginan is being used to validate and verify the quality of data coming from the NPIC network, ensuring that consumers are only accessing data that can be trusted.
Ginan is also being used to generate models of error sources in real-time that are broadcast over the internet as an openly accessible correction service - available for research and innovation.
Geoscience Australia's GitHub page provides access to the latest version of Ginan. Please be aware that the developers continuously update this software with new functionality and quality improvements.
This diagram illustrates how Ginan integrates with NPIC’s network of positioning infrastructure and provides correction data to users through an internet connection
The name Ginan comes from the Wardaman people, traditionally living in the region south-west of Katherine in the Northern Territory. Ginan is a Wardaman word for a red dilly-bag filled with songs of knowledge and the fifth-brightest star in the Southern Cross. Just as the Southern Cross helped the First Australians to navigate this land, the positioning capability developed by Geoscience Australia will provide information on exactly where we are and where we are going.
The latest version of Ginan can be accessed through Geoscience Australia’s GitHub page. Please note that this software is continuously updated with new functionality.
About Ginan, GNSS Analysis Centre Software
Ginan is a suite of open-source tools that are used to analyse GNSS data in real-time. Users are able to download and use the tools as a whole, or download and customise certain elements to meet their individual specific need.
- Ginan
- promotes Australia’s unique modelling and analytic systems for multi-GNSS processing in real-time and delivers precise positioning products to the Australian and international PNT community
- supports expert advice on navigation system performance over Australia
- provides a state-of-art suite of open-source tools to analyse GNSS data to universities and research organisations, to enable Australia to lead the development of geospatial technology.
- By making the tools open-source, Geoscience Australia is:
- supporting GNSS education by allowing students and researchers to examine how the GNSS Analysis Centre Software algorithms work to solve complex problems
- enabling researchers and commercial organisations to use the tools to solve research or commercial problems.
The interoperable nature of the tools allows and encourages users to develop innovative position-dependent technology and services that could be of economic benefit to Australia. This will grow the market for equipment manufacturers, technology integrators, service providers, the science community and end users enabling them to realise the full benefits of GNSS.
Ginan uses the processing method called UnDifferenced/UnCombined (UDUC), which improves accuracy by estimating certain errors. It can determine precise satellite orbits and handle data more effectively, removing unnecessary noise and errors for better analysis outcomes.
The software provides robust data filtering capabilities, which means it can identify and remove anomalies like signal interruptions or outliers. This ensures that the processed data is of high quality and reliable.
How to get access
You can access the data streams and products (files and correction messages) in real-time to enable precise positioning from the GNSS Data Centre. The latest version of the software is available under an open-source licence from Geoscience Australia’s Github.
If you would like to stay informed about software developments and updates, you can subscribe to Positioning News, which is Positioning Australia’s regular email newsletter.
How it works
GNSS satellites operate in a dynamic and complex space environment, and their positioning and timing signals pass through the atmosphere to reach Earth. The satellite systems, the space environment, and the atmosphere all influence the satellite signal, resulting in potential errors in positions determined by ground receivers. Uncorrected signals provide accuracy only up to 5–10 metres.
Ginan functions as a super GNSS processing engine that applies models of the Earth's gravity (Earth tides) and Atmosphere to generate corrections for potential errors, which drives down the uncertainty on the parameter of interest.
The Ginan tools take signal data from multiple satellites and constellations and combines it with predictions from the models to produce a correction signal. When users apply this signal with a GNSS receiver, it reliably enhances the accuracy of calculated positions to within a few centimetres.
For frequently asked questions and answers, please see the FAQ page: