Positioning Australia National Positioning Infrastructure Capability (NPIC)
Page last updated:21 September 2023
A unified approach to positioning infrastructure
Precise positioning technologies are embedded across many industry sectors. In Australia these technologies are being used to grow our food, build our roads, and keep our communities safe.
To obtain precise positions, observations from navigation satellite systems (such as the Global Positioning System – GPS) need to be corrected for a range of errors introduced by the atmosphere and the dynamic nature of the satellites. These corrections are derived from networks of ground-based positioning infrastructure with precisely known coordinates.
Through the National Positioning Infrastructure Capability (NPIC), Geoscience Australia is unifying the management of and opening access to Australia’s positioning infrastructure. This ensures that consistent, fit-for-purpose positioning data and services are available to government, industry, and academia.
The benefits of NPIC
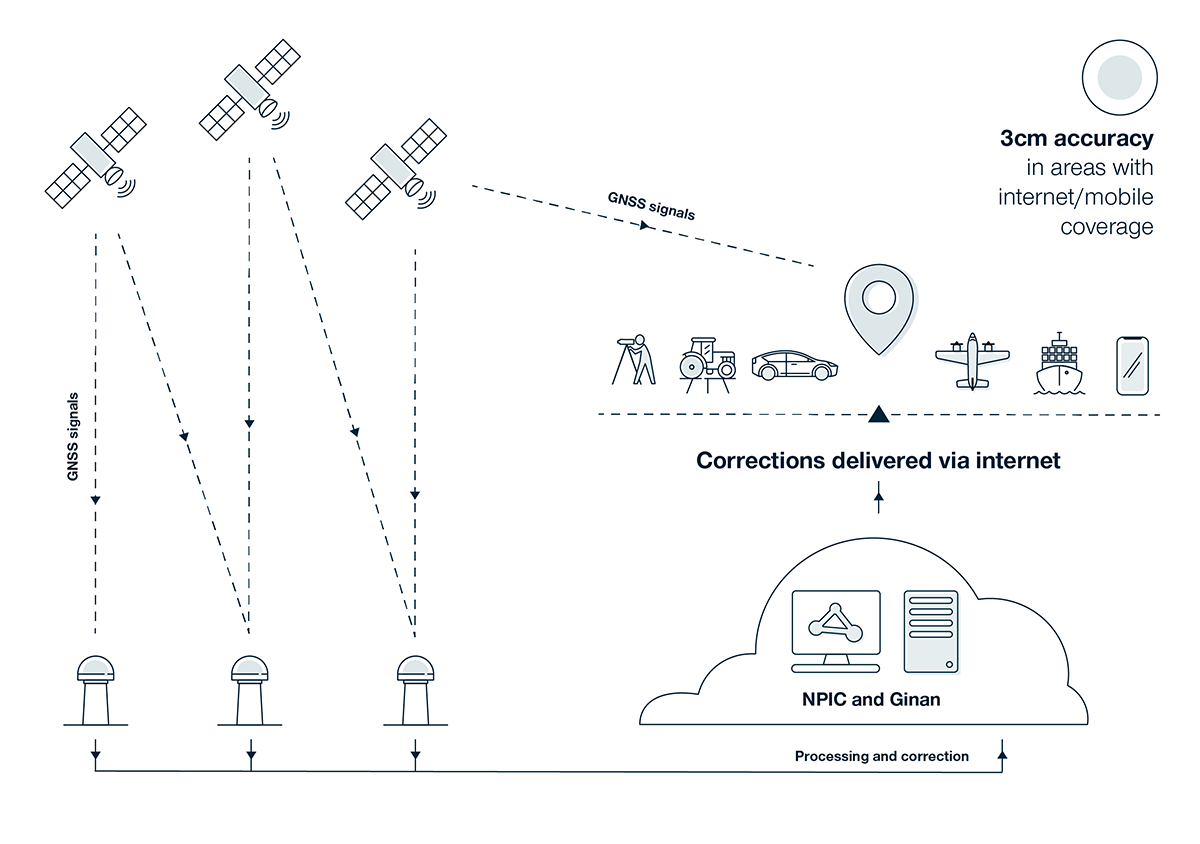
By establishing a unified national network, NPIC is enabling the delivery of centimetre accurate positioning services across Australia in areas of mobile phone coverage.
Through NPIC:
- Consumers have access to high-quality data from trusted reference stations.
- Coverage of positioning services is increased and consistent between commercial service providers.
- Service providers can offer flexible, cost-effective positioning services to a range of users across industry sectors.
An independent Economic impact of the National Positioning Infrastructure Capability program [PDF 4.7 MB] found that NPIC is estimated to deliver $545 million in benefits, with $365 million in direct benefits to the agriculture, mining, construction, and surveying and mapping sectors, across the entire economy over 2018–19 to 2037–38, creating over 2,300 full time jobs nationwide by 30 June 2038. More information available in the following news story.
See the summary report, Economic impact of the National Positioning Infrastructure Capability program [PDF 914.4 KB], by ACIL Allen.
About NPIC
NPIC is part of the Australian Government’s investment into building a world-class satellite positioning capability.
NPIC is operating and maintaining the infrastructure and digital systems to enable a centimetre accurate positioning capability in areas of mobile phone coverage.
To achieve this Geoscience Australia has:
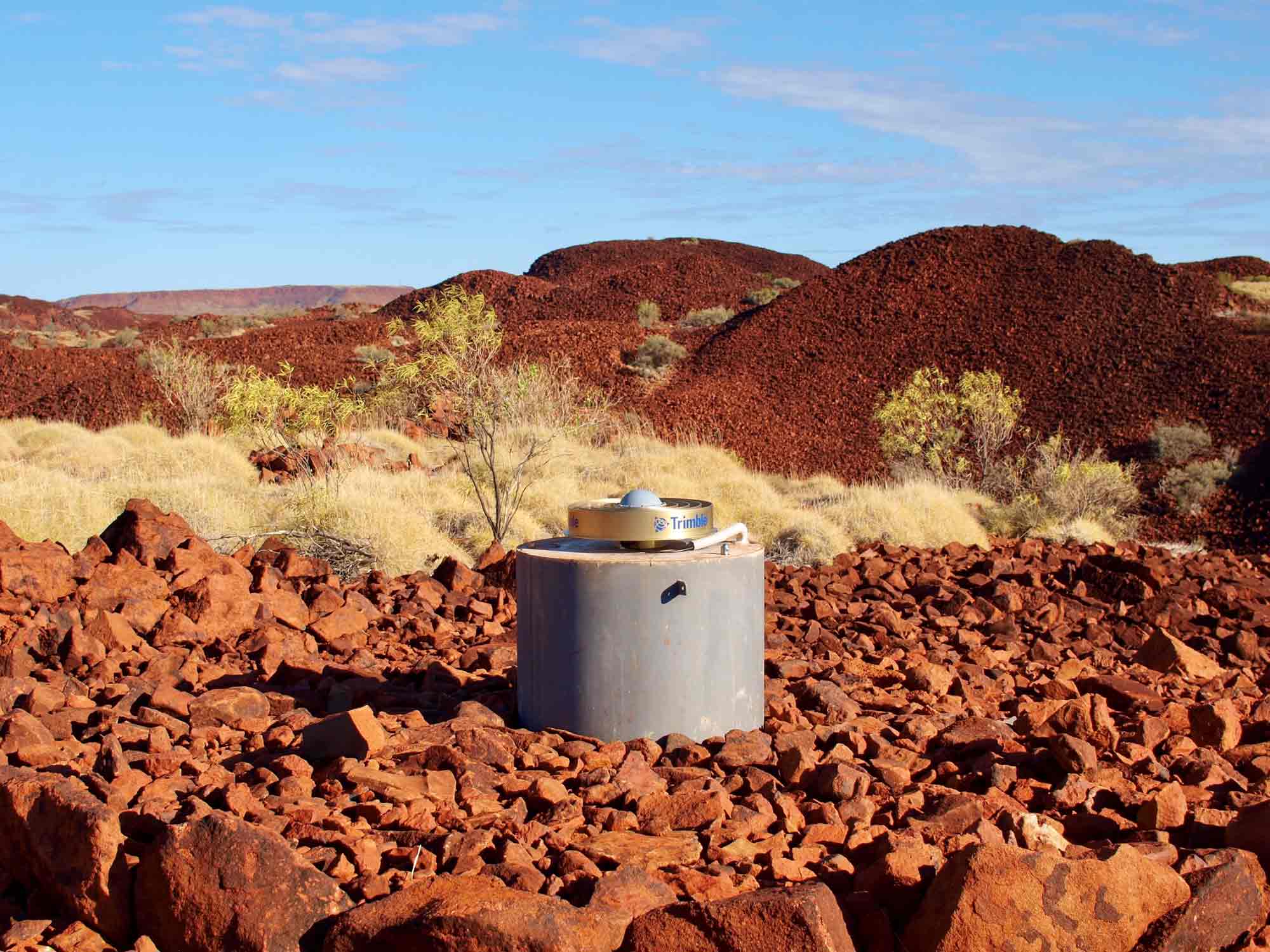
- Modernised and expanded the Australian Regional GNSS Network (ARGN), which provides the geodetic framework for all spatial data in Australia.
- Established data sharing agreements with government and commercial operators of positioning infrastructure, to open access to the data streams from over 500 stations.
- Established secure digital platforms to collect, validate, and disseminate the positioning data and services.
Precise positioning from GNSS ground reference stations offers high levels of accuracy for specialist users
How NPIC works
- Geoscience Australia collects GNSS data streams from select government and commercially operated reference stations.
- The data streams from these reference stations are validated and verified using our multi-GNSS analysis toolkit – Ginan.
- The validated data streams are openly available to government, industry, and academia to support scientific and societal applications.
- Many industry partners value-add to these data streams to deliver centimetre accurate positioning services across Australia.
In addition, Geoscience Australia provides two open centimetre-accurate positioning correction services – a single-base Real Time Kinematic (RTK) service and a state space representation (SSR) correction service. These services can be accessed by receivers or software that can handle corrections delivered over the internet using the Network Transport of RTCM over the Internet Protocol (NTRIP). Access to these streams requires a free account, to register visit the GNSS Data Centre Portal.