Derived data product DEA Fuel Moisture Content
Page last updated:14 October 2025
Overview
The Digital Earth Australia Fuel Moisture Content (DEA FMC) product provides high-resolution, satellite-derived insights into the moisture content of live vegetation across Australia by calculating the percentage of water mass relative to dry mass in living vegetation. Developed by DEA in partnership with Australian National University’s (ANU) Bushfire Research Centre of Excellence, this product supports fire preparedness, land management and sustainability by helping users assess timely information on fuel moisture condition.
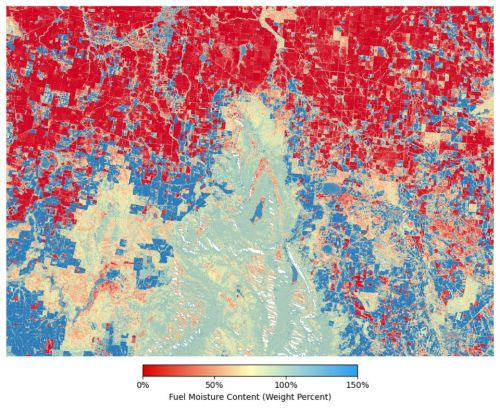
Image: This image depicts Fuel Moisture Content values over the Grampians National Park and surrounding farmland in May 2020. Areas of native vegetation have values from 50% to 100% moisture content and are coloured in orange, yellow and pale blue, respectively. Dormant fields and pastures have low moisture values, below 25% while the very dark blue areas have a moisture content of 150% - 300%, these indicate pastures where lush green grass remains at the end of autumn.
Why measure fuel moisture?
Australia’s hot, dry climate and vast bushland make it one of the most fire-prone regions on Earth. Understanding vegetation dryness is essential for anticipating and managing bushfire risk.
Fuel Moisture Content (FMC) is a metric used to understand flammability and fire risk. FMC describes the amount of water contained within the leaf material of plants and it varies from season to season. FMC is traditionally determined by collecting plant samples in the field and analysing them in a laboratory. DEA FMC is a remotely sensed proxy for this measurement. Based on satellite imagery, it provides consistent, continent-wide information on fuel moisture condition. DEA FMC can be used in combination with other information provided by emergency management, land managers, and researchers to understand vegetation flammability and fire potential.
Key features
- High-resolution data: 20-metre spatial resolution across the Australian continent
- Operationally ready: Designed for integration into workflows for fire risk assessment, mitigation planning, and environmental monitoring.
- Open access: Freely available via DEA Maps, DEA WMS, and the DEA Knowledge Hub
Applications
- Monitoring and mapping the dryness of vegetation across different landscapes
- Predicting and assessing vegetation flammability and fire risk, spread and intensity
- Modelling fire risk over time and across different ecosystems with changing climate conditions
- Prioritising and evaluating fire, forestry and utility agency management based on the dryness and fire risk of vegetation
- Helping to plan safer hazard-reduction burns from 250-metres down to 20-metre grid size on the ground.
Access the data
Discover how DEA FMC can inform better decision-making for fire risk, land management and sustainability:
Get involved
Be part of shaping DEA FMC by providing your feedback and use cases to help shape future iterations. If you have questions or would like to share your experience, please contact earth.observation@ga.gov.au.